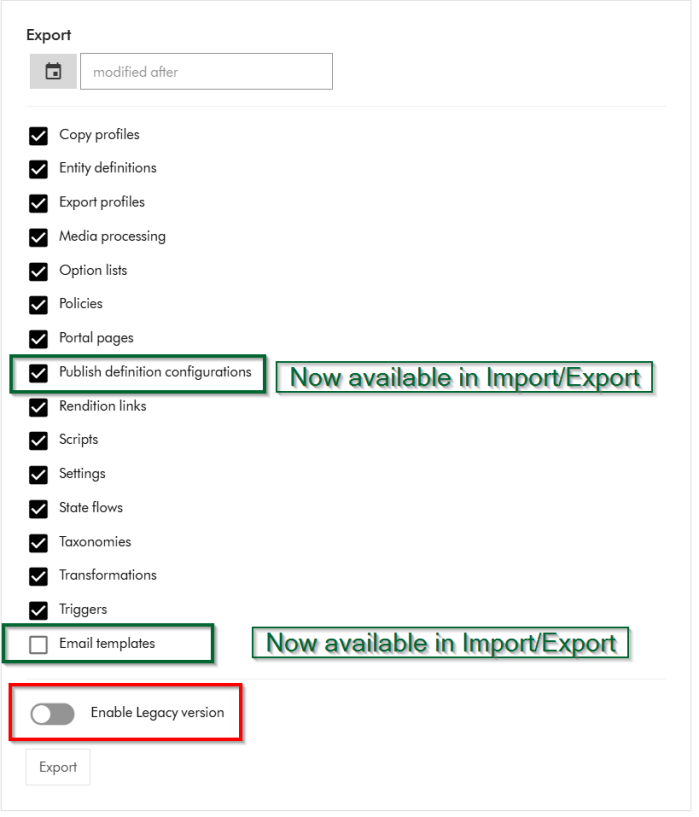
Context and background
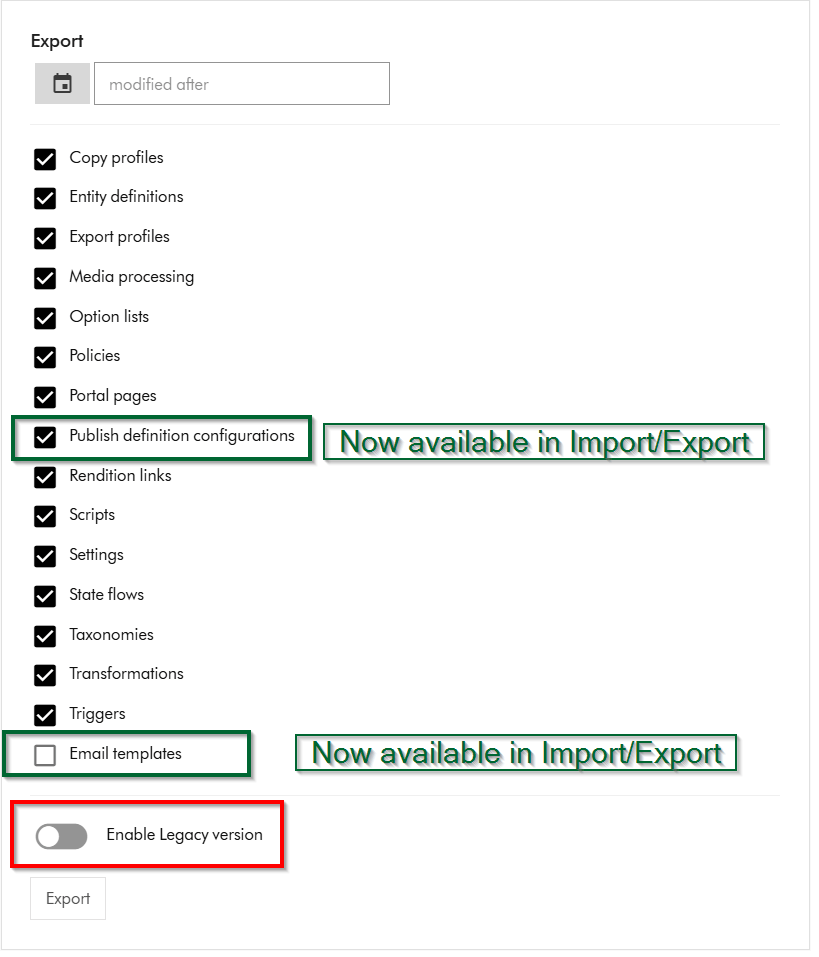
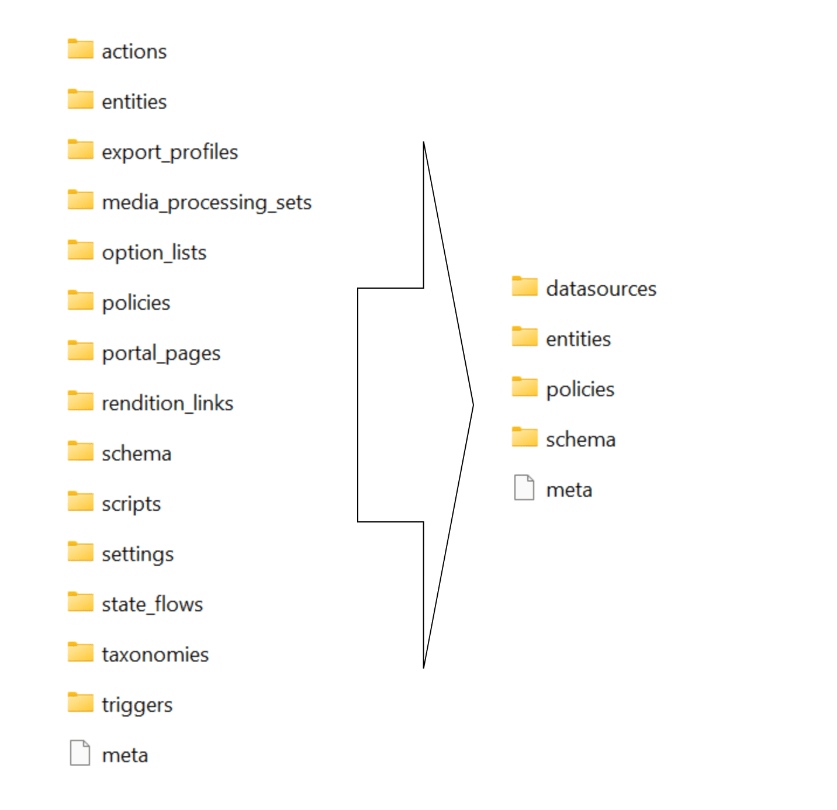
Content Hub now has a new Import/Export engine (version 2) which should now be the default in your environments. Sitecore have updated the underlying Content Hub packaging structure to organise content by resource type rather than by export category as it was previously the case. This change makes navigation more straightforward and ensures greater consistency throughout the package. You can read more about the changes introduced in my previous blog post where I took a deep dive into the changes and impact on CI/CD pipelines.
While refactoring CI/CD pipelines to work with the new Import/Export engine in early January, I came across two main blockers which at the time meant I couldn’t progress any further.
That is when I reached out to Sitecore Support and raised two product issues, which Sitecore recognized and embarked on fixing them. These issues were MONE-55068 (support ticket CS0655802) and MONE-55007 (support ticket CS0655833).
The great news is that Sitecore are doing a fantastic job in channeling resources to get these fixes out of the door. In less than a month, we have fixes to the two issues above plus additional fixes that were shipped on February 6, 2026. This is incredible work from Sitecore!
Support ticket CS0655802 and product issue MONE-55068
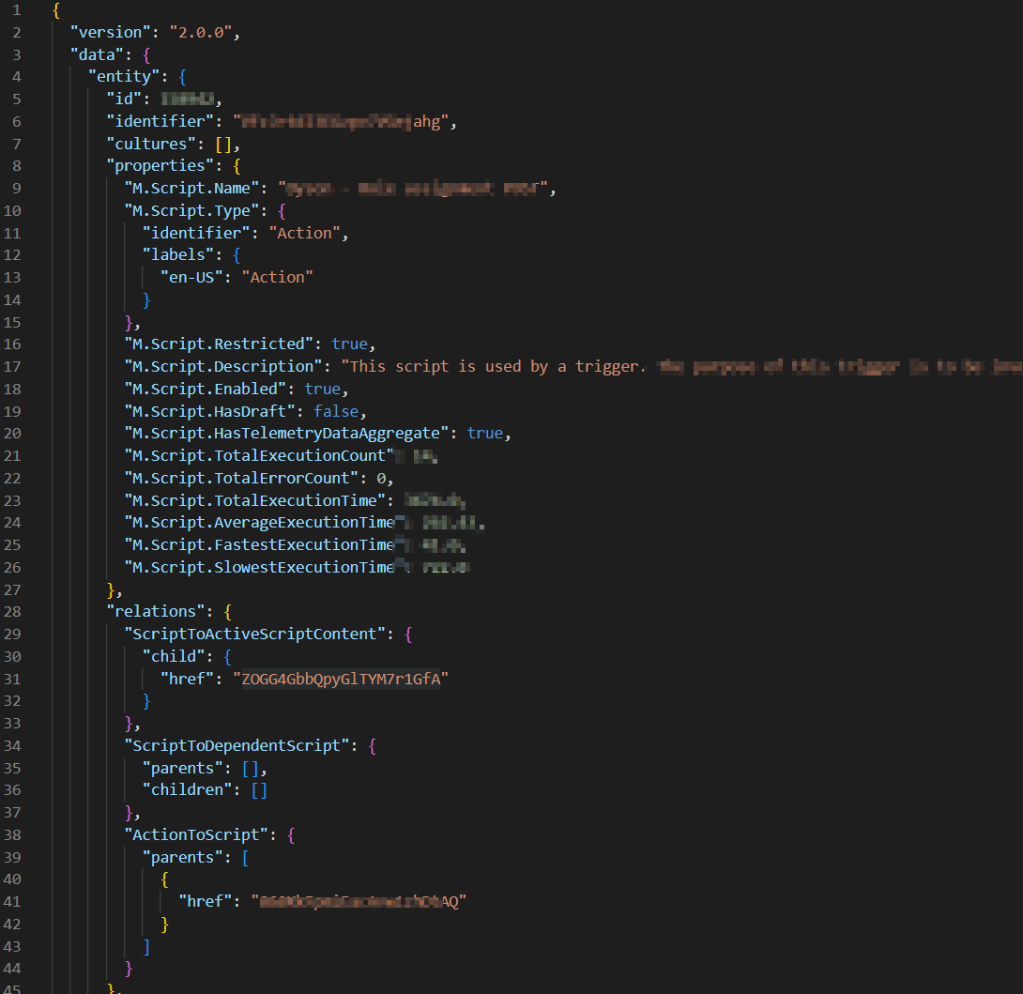
Below is a screenshot from the issue I encountered when importing a brand new Taxonomy definition.
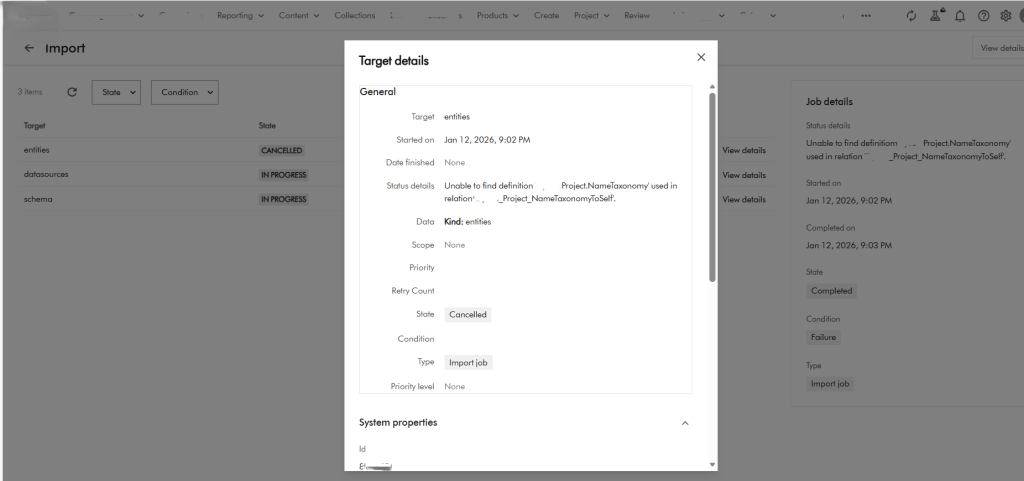
The raw error message is also shown below
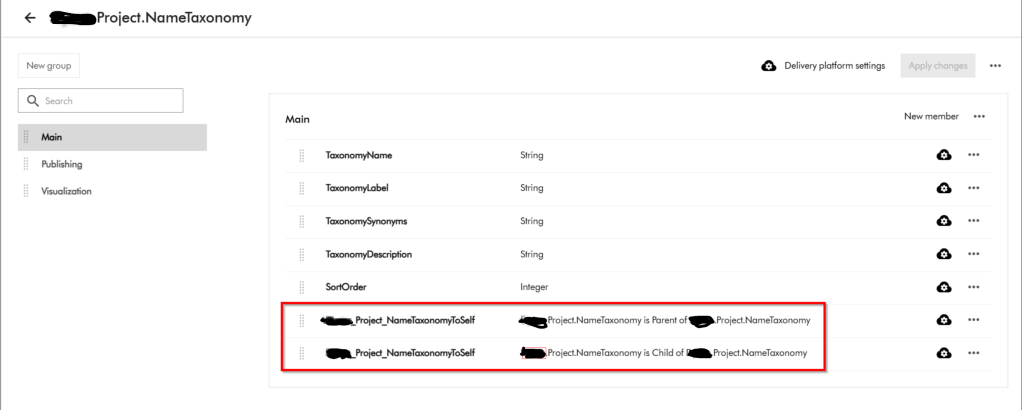
Raw Output: xxxx Details Unable to find definition 'XXXX.Project.NameTaxonomy' used in relation 'XXXX_Project_NameTaxonomyToSelf'. filename: entities.zip import_type: Package import_dry_run_feature: True Targets Target: entities Status details: Unable to find definition 'XXXX.Project.NameTaxonomy' used in relation 'XXXX_Project_NameTaxonomyToSelf'. Kind: entities Target: datasources Status details: Kind: datasources Target: schema Status details: Kind: schemaThis was a clear defect within the Product since we know Taxonomy entities have self-relations and therefore should not be the reason a taxonomy entity will fail to import successfully. Below is my taxonomy definition
Fix provided by Sitecore
Fixed an Import/Export v2 issue that caused an error when importing packages with new definitions. (MONE-55068)
Support ticket CS0655833 and product issue MONE-55007
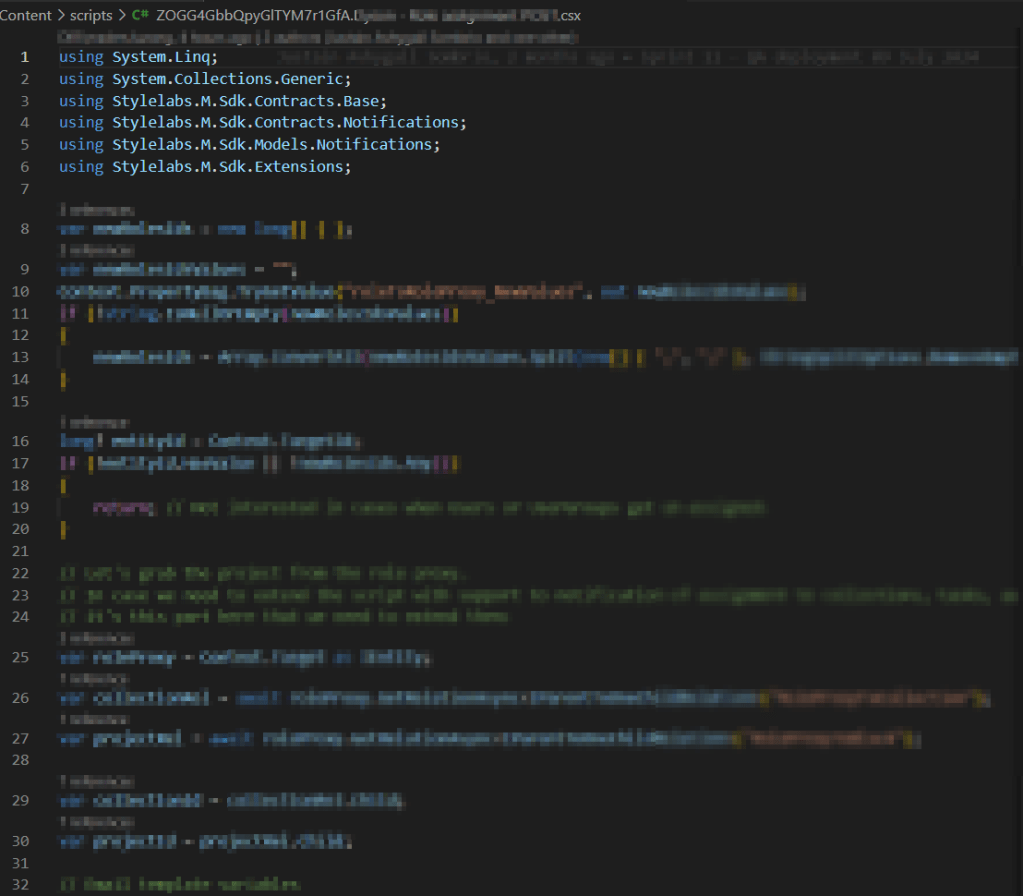
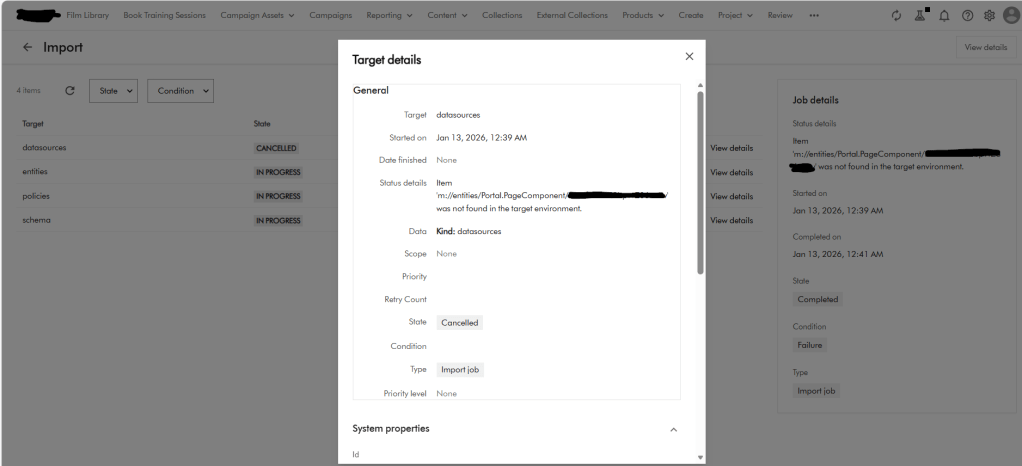
Below is a screenshot of the error I encountered when using CLI to import Pages. This error seems logically related to one above affecting self-relations in taxonomy definitions.
For pages, the issue was caused by one of the components related to the parent page not existing and causing the page import to fail. You could have thought the Import/Export engine should resolve dependencies, but clearly this was a Product issue.
Fix provided by Sitecore
Fixed an Import/Export v2 issue that caused an error when importing Creation components linked to Search components. (MONE-55007)
Support ticket CS0648899 and product docs issue MDOC-5887
While refactoring the CI/CD I noticed lack of sufficient documentation to detail what was changed in the new packaging architecture as part of Import/Export v2. I raised another support ticket CS0648899 with Sitecore, which was duly registered as MDOC-5887 to provided the needed clarity in the official docs.
I am happy to report that Sitecore have also addressed the documentation gap and fixed the MDOC-5887
Other resolved issues with Import/Export v2 engine
Below are the three other fixes shipped on February 6, 2026
- Import/Export v2 now excludes
M.Portal.Versionentities when exporting to prevent missing-entity errors during import. (MONE-53876) - Import/Export v2 now correctly preserves and updates user group names with leading or trailing whitespace during import, preventing duplicate groups and import failures. (MONE-54335)
- Import/Export v2 operations no longer swap labels between parent and child when the relation name is the same and there are no actual changes in the imported package. (MONE-54614)
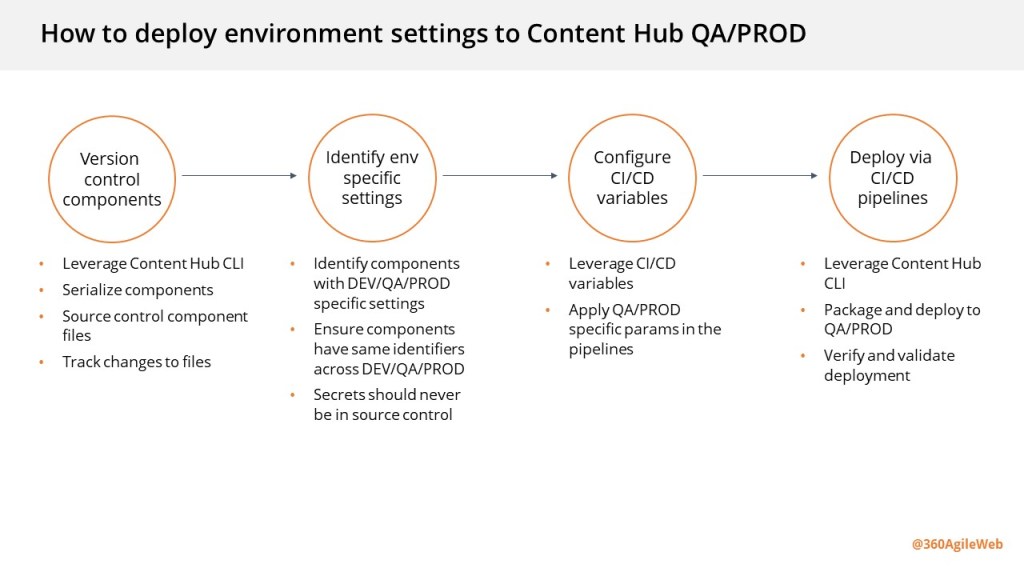
Updating your CI/CD pipelines
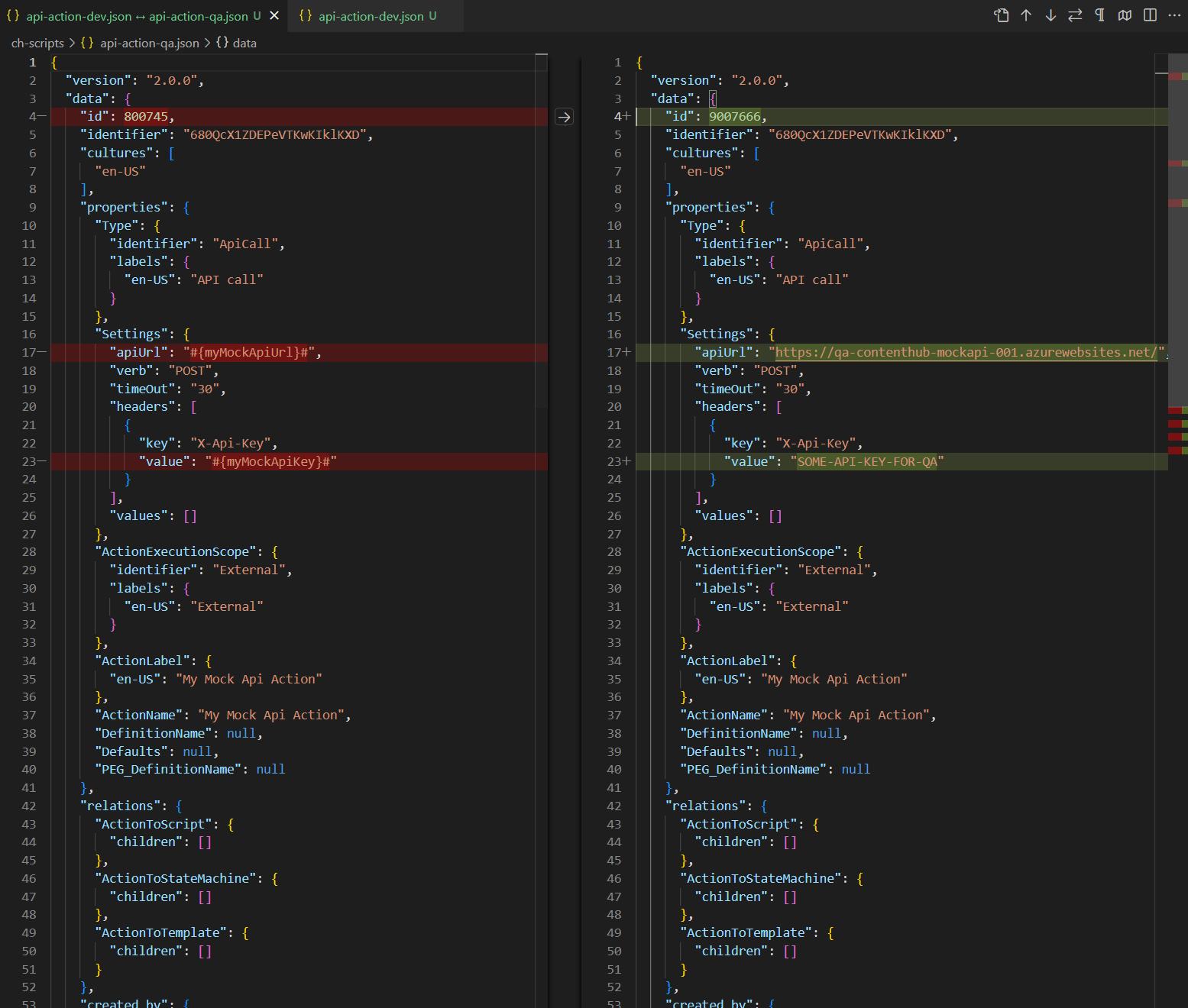
As already covered in my previous post, it is very straight forward to update your existing CI/CD pipelines to work with the new package architecture. In simple terms, you will need to simply map your previous logic to work with the new package architecture. Ensure your Content Hub environments are re-baselined within your source control as well.
Next steps
In this blog post, I have looked at the list of issues that Sitecore have resolved for the new Content Hub Import/Export engine. I also dived into my two support tickets that I had raised that were affecting the Import/Export v2, thereby contributing to Product enchantments. I noted and appreciated how quickly Sitecore teams worked to resolve these issues within a month. I hope your Content Hub CI/CD pipelines are more robust with all these fixes going forward.
Please let me know if you have any comments above and would like me to provide further or additional details.